- Article
Comparative Evaluation of Mucosal Adjuvants for Intranasal Immunization with a Recombinant RSV Prefusion F Protein
- Hongqiao Hu,
- Lei Cao and
- Yan Zhang
- + 5 authors
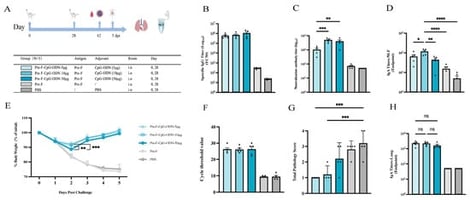
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) remains a major etiologic agent of acute lower respiratory tract infection (ALRTI). Currently licensed RSV vaccines are administered by intramuscular injection and induce limited immunity at the respiratory mucosal interface, underscoring the need for effective mucosal vaccination strategies. Methods: To enhance mucosal immune responses, we used prefusion F protein (Pre-F) as the antigen and performed intranasal immunization in BALB/c mice. Four mucosal adjuvants (CpG-ODN, CTA1-DD, IFN-α, and PEI) were systematically compared across different dose levels to evaluate their immunological and protective efficacy. Results: Both adjuvant type and dose helped shape the magnitude and quality of the immune response and the level of protection. CpG-ODN showed a dose-restricted immunopotentiating effect: an intermediate dose (10 µg) significantly increased neutralizing antibody titers and nasal mucosal IgA responses, improved post-challenge body weight recovery, and reduced lung viral load, whereas higher doses provided no additional benefit and were associated with aggravated lung pathology. PEI and IFN-α exhibited dose-dependency within a certain range, but increasing doses did not result in further improvements in immune responses or protection; an intermediate dose (10 µg) was sufficient to elicit robust systemic and mucosal immunity. CTA1-DD improved selected immune parameters at appropriate doses, yet its overall immunopotentiating effects remained modest. Direct comparative analysis using the representative doses selected from the three dose levels for each adjuvant indicated that 10 µg CpG-ODN or PEI provided superior immunogenicity and protection, whereas PEI induced a Th2-biased immune profile at both humoral and cellular levels. Conclusions: These findings highlight that favorable immunogenicity and protection are achieved within defined dose windows rather than at maximal doses. Among the adjuvants studied, low-to-intermediate doses of CpG-ODN, particularly 10 µg, show strong potential for intranasal mucosal immunization with recombinant RSV Pre-F protein. By systematically comparing dose–effect profiles across multiple mucosal adjuvants, this study offers comparative insights into adjuvant selection and dose selection for intranasal RSV vaccine development.
16 February 2026